Medisafe Platform, App Increase Medication Adherence
The following originally appeared in Population Health News July 2017 issue (Volume 4, Issue 7), published by Health Policy Publishing, LLC.
Objectives:
- Evaluate the impact of Medisafe on a cohort of patients with hypertension, hyperlipidemia or
- Evaluate the uses of digital technology for managing chronic illnesses
Program Description: Founded in 2012, Medisafe is a leading cloud-based mHealth platform for medication management, helping users worldwide adhere to even the most complicated medication schedules. It helps stakeholders across the care continuum better leverage their limited time and resources to achieve improved medication adherence. Medisafe is approaching four million patient and caregiver users, with more than 650 million medication doses managed worldwide.
Three-fourths of adults are non-adherent in one or more ways, placing an economic toll on the U.S. healthcare system of $100 billion annually. The average adherence rate (the degree to which patients correctly follow prescription instructions) for medicines taken only once daily is nearly 80%, compared to about 50% for treatments that must be taken four times a day. As many as 75% of patients (and 50% of chronically ill patients) fail to adhere to or comply with physician-prescribed, treatment regimens.[1]
The app does the following:
- Educates users about their medications and
- Offers helpful
- Reminds them to take their prescriptions on time every
- Provides alerts for
- Shares progress, enabling users to send results to their
- Synchronizes a family’s pillboxes in one place in real
- Curates tailored prescription coupons and special offers at drugstores, such as CVS and
- Tracks measurements, including blood glucose, blood pressure, cholesterol levels, peak flow and pulse, and shares them with providers on a dashboard.
The Medisafe app uses a pillbox design segmented into four daily quadrants so consumers will know which medications they have taken and which ones are next. In addition, it can be linked to a wireless pill bottle so when a consumer opens the bottle and takes a medication, it will be recorded in the Medisafe app.
IMS Health decided to study Medisafe’s impact on patients with hypertension, hyperlipidemia and diabetes due to the prevalence of these conditions in the U.S. population and because these conditions are precursors to major health complications, including stroke and kidney disease, when left untreated. IMS Health acknowledged Medisafe’s ability to improve the adherence prior to the completion of the study.
“Even before the conclusion of this study, IMS Health’s AppScript team recognized Medisafe as the highest rated medication management app in terms of AppScript Score as seen in our recent IMS Institute for Healthcare Informatics report, Patient Adoption of mHealth,” says Brian Clancy, senior product manager, IMS Health AppScript. “When our team examined the data of Medisafe users versus non-Medisafe users, it became clear that the application was making a significant improvement in medication adherence.”[2]
The study period ran from Oct. 1, 2013 through June 30, 2015, with an index period of Oct. 1, 2014 through December 31, 2014. regular basis. Retail clinics swiftly and efficiently treat uncomplicated minor illnesses and provide preventive care such as vaccinations at minimal expense.
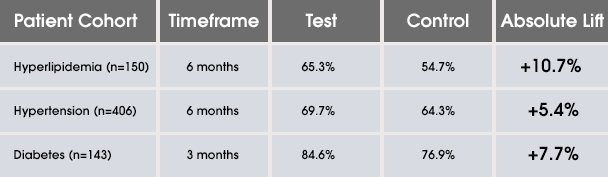
Evaluation Process: Patients entering a dose for antihypertensive or cholesterol-lowering medications over the course of the study were matched 1:1 to non-app users who functioned as a control group. These non-app users were anonymously matched via prescription claims in the IMS de-identified prescription database. The study included 406 patients taking anti- hypertension medication and 150 taking cholesterol-lowering medication, as well as a matching control group.
The mean age of the patients considered in this study was 52.5 and 54.6 for anti-hypertension and cholesterol-lowering users, respectively. The cohort was roughly an equal ratio of male to female. Of the anti-hypertension patients, 7.9% were new to medication therapy, while 7.3% of the cholesterol-lowering users were new. The rest were continuing with previously established regimens.
Results: The study calculated persistence of hypertension/lipid levels during the six months, post-index period using a 10-day refill gap past the end of a day’s supply of the previous prescription. The study shows that Medisafe users taking cholesterol-lowering or anti-hypertension medication had an improved persistence compared to matching control groups. The relative increase in adherence over six months was 8.4% for anti-hypertension patient users and 19.5% for hyperlipidemia patient users.
Results demonstrated a statistically significant increase across the chronic conditions tested. Comparing app users to all controls at six months, users with hyperlipidemia had a 10.7% (65.3% vs. 54.7%, p=0.03) lift in medication persistence, and users with hypertension had a 5.4% (69.7% vs. 64.3%, p=0.05) lift in medication persistence. Users with diabetes had a 7.7% (p=0.05) lift over a three-month period.
Lessons Learned
- Use of mobile technology supports medication adherence and can lead to better control over chronic
- Study bolstered results of a previous Medisafe study on the impact of its solution for Stage 1 and 2 hypertension users who were also using a connected blood pressure cuff and saw an average 19.3 mmHg reduction in their systolic blood
[1] “Improving Prescription Medication Adherence Is Key to Better Health Care.” PhRMA. January 2011.
[2] Medisafe Demonstrates Multi-Month Adherence Lift in Study by IMS Health.” Medisafe. Oct. 29, 2015.
