Study: Navigating the Flooded Adherence App Marketplace: Rating the Quality of Medication Adherence Apps
To view the original study, click here.
Study rationale and Background
Medication nonadherence leads to an estimated 125,000 deaths and costs $100 billion annually in the US. There is a vast pool of tools, including medication adherence apps, which are now available to help patients manage their regimens. However, many of these apps available with varying degrees of functionality and health literacy compliance, making it difficult to identify quality apps. The goal of this study is to assess the available applications based on performance.
Methodology
- Conduct marketplace search for medication adherence apps in June 2014
- Inclusion criteria:
- English language apps with medication reminders
- Apps capable of handling multiple disease states and medication
- All researchers must be able to install app
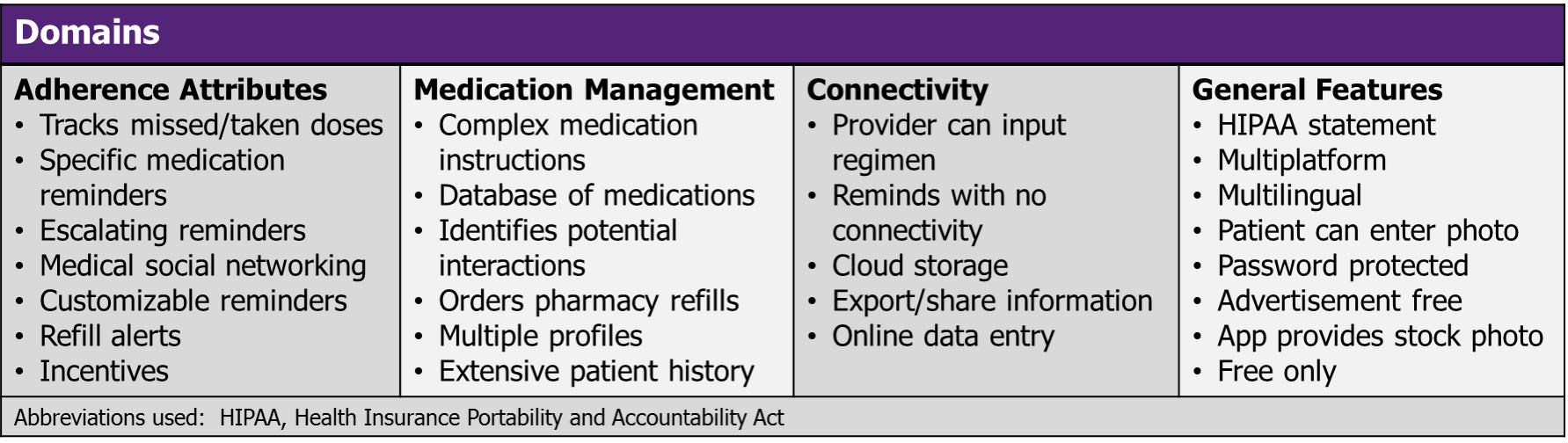
- Developed 28 author-identified desirable app features across four domains assessed from developer descriptions with each feature assigned a score of importance (1-modest; 2-moderate; 3-high)
- Each app was evaluated over a four day period using a standardized six drug regimen: vitamin E once daily, diltiazem twice daily, simvastatin once daily at bedtime, azithromycin once daily for three days, prednisone three day taper, and alendronate once weekly
Domains assessed:
Study results
-
Of the 100 apps eligible for testing, 19 were excluded because they failed to produce medication reminders or could not be installed by at least one author, which included all of the Blackberry apps, leaving 81 apps for testing
-
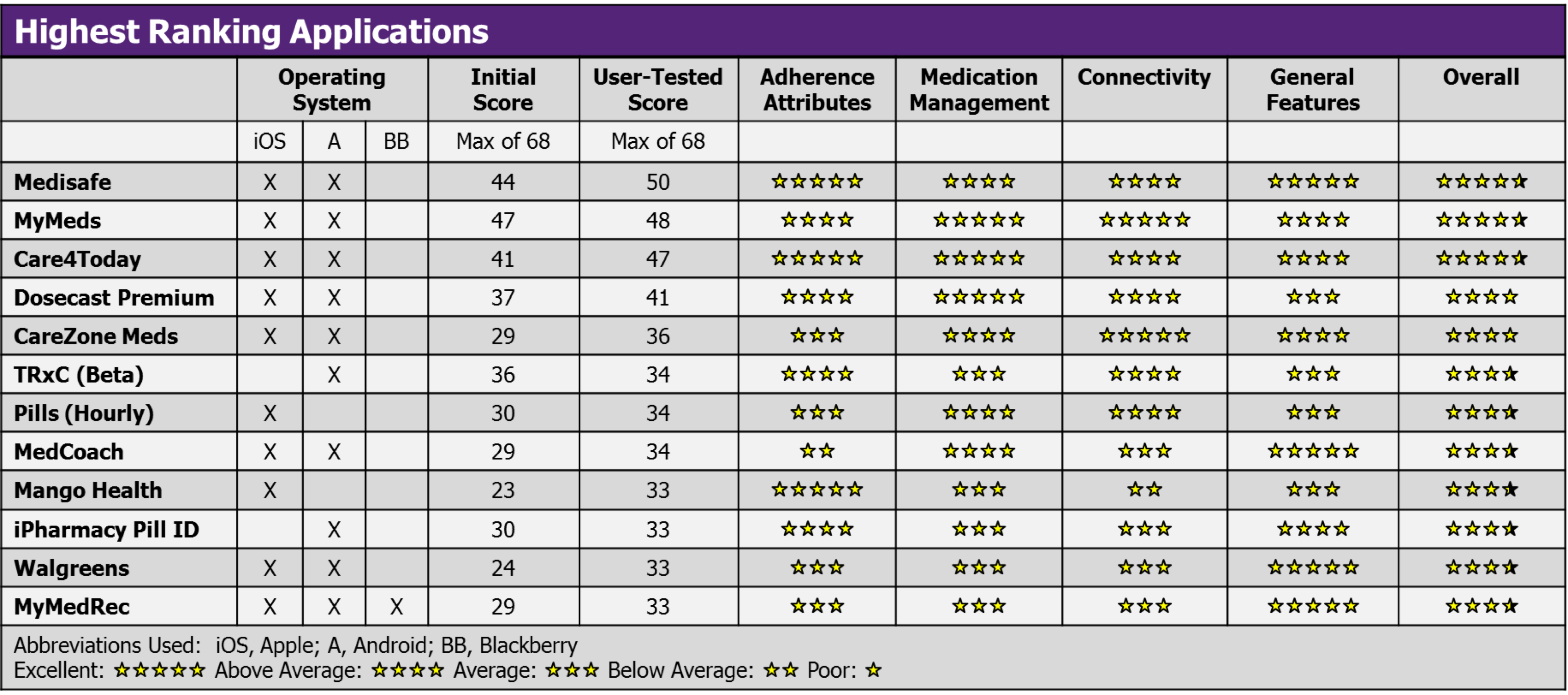
The mean user-tested score was 27 and ranged from 13-50 (max of 68)
-
Compared to the initial scores, 39 (48%) user-tested scores increased, 35 (43%) user-tested scores decreased, and 7 (9%) user-tested scores were unchanged
Conclusion and Recommendations
- The medication adherence app market has more than doubled in the past two years and continues to offer apps with high variability in terms of app quality
- No app possessed all desirable author-identified features; however, several apps were highly rated across all four domains
- Sharing this information with healthcare providers and consumers could enable them to find a quality app that may improve their medication adherence
- Development of a searchable adherence app website in order to alleviate the frustrations of identifying quality apps in the online marketplaces
- App effectiveness could be diminished if designed without health literacy in mind; therefore, the addition of a health literacy domain could help in identifying apps with the highest patient usability
Acknowledgements:
Presented by: Catherine Renna, Rebecca Shilling, Seth Heldenbrand, PharmD, Lindsey Dayer, PharmD, BCACP, Bradley C. Martin PharmD, PhD
Presented at: American Pharmacist Association Annual Meeting and Exposition, 2015